Cultural Landmines: One Misstep Can Cost You Millions
A 2018 M&A report from Mercer (now part of Marsh McLennan) found that 30%
of transactions fail to ever meet financial targets due to cultural issues.
That was during relatively stable times. Today, global companies are navigating geopolitical instability, supply chain disruptions, shifting market dynamics, and high-stakes cross-border relationships — a volatile mix where cultural landmines often go unnoticed until the damage is done.
“Culture hides more than it reveals, and strangely enough what it hides,
it hides most effectively from its own participants.”
— Edward T. Hall, The Silent Language (1959)
Culture and the Power of Perception
Ask ten people to define culture, and you’ll likely get ten different answers. Some might focus on traditions, language, or food. Others may speak of shared values, beliefs, or customs. And all of them would be right — partially.
But here’s the challenge:
We don’t just observe culture — we interpret it. And often, we do so through the lens of our own experience.
Perception plays a powerful role in how we engage across cultures. We make assumptions, draw conclusions, and form judgments — all shaped by the “water” we swim in. That’s why cultural misunderstandings can feel so subtle, yet cause such significant impact.
To better understand culture, we must first recognize how invisible it can be — especially our own.
Which brings us to one of the most useful ways to think about culture:
👉 The fishbowl.
Cultural Awareness Begins with Self-Awareness
🎯 When culture is misunderstood, the consequences can be costly. Explore our Global Marketing Blunders page to see how leading brands have misstepped — and what it teaches us about cultural intelligence.
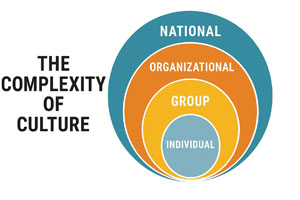
Why Culture Is a Multi-layered Framework — Not a Checklist
Contact us today to explore how our training and coaching solutions can equip your team to succeed — whether you're tackling global initiatives or navigating complex cross-cultural challenges. We welcome the opportunity to support your goals — across cultures, across borders, and across the global landscape.
HOME | SERVICES | CULTURAL INTELLIGENCE | EXPLORE CULTURES | INSIGHTS | ABOUT | CONTACT
Email Us | www.culturalsavvy.com | ©1999–2025 Cultural Savvy. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use